카테고리 없음
Heart disease, Cardiac disease - Mitral stenosis
jbook
2022. 2. 8. 00:21

[ mitral stenosis ]
Definition
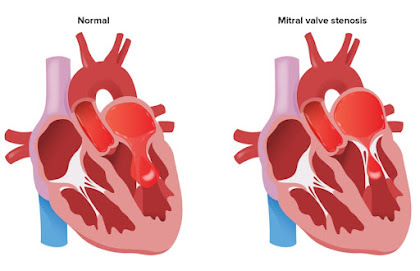
The mitral valve is located between the left atrium and the left ventricle, and serves to prevent the backflow of blood entering the left ventricle into the left atrium. A disease in which the mitral valve narrows is mitral stenosis. The flow of blood from the left atrium to the left ventricle is blocked, causing the left atrium to expand, and breathing difficulties appear during exercise. If it worsens, breathing difficulties may occur even at rest. Arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation may occur due to dilatation of the left atrium. It occurs more frequently in women than in men, and is often accompanied by mitral regurgitation.
Cause
In more than 90% of cases, valve damage progresses as a complication of rheumatic fever. In some cases, it is caused by congenital mitral valve disease.
Symptom
Symptoms of mitral valve stenosis usually appear slowly. Typical symptoms caused by left ventricular dysfunction are dyspnea during exercise, sitting respiration (breathing in a sitting state because breathing is difficult while lying down), paroxysmal nocturnal breathing difficulties, fatigue, etc. In addition, as the blood that has not flowed into the left ventricle accumulates in the left atrium, the left atrium dilates, and irregular pulses called atrial fibrillation cause palpitations.
When a blood clot leaves the heart and blocks a blood vessel in the brain, a stroke occurs. Over time, symptoms of right ventricular insufficiency such as peripheral edema, hepatomegaly, and ascites may develop. Rarely, when accompanied by severe left atrium dilatation, the laryngeal nerve is compressed and the voice stops.
Treatment
Asymptomatic and mild mitral stenosis does not require treatment, and prevention of recurrence of rheumatic fever and infectious endocarditis is essential. Patients with mild symptoms are stable for a considerable period of time until treatment is required, so they are followed up every year or every other year. Percutaneous mitral valve dilatation may be considered for symptomatic or moderate to severe mitral valve stenosis patients, and diuretics, antiarrhythmic drugs, and anticoagulants are administered as needed to relieve symptoms. If you have symptoms of heart failure, you should follow a low-sodium diet.
Percutaneous mitral valve dilatation is a treatment method in which a catheter with a balloon is placed between the narrowed mitral valves through a blood vessel, and then the balloon is inflated to widen the mitral valve with stenosis. The success rate of such plastic surgery for mitral stenosis is lower than that for mitral regurgitation. The reason is that most of the mitral valve stenosis is caused by rheumatic fever. Rheumatic fever invades the valve and subvalvular structures as a whole, not just one part of the valve, causing fusion of the commissure part, tendonitis and papillary muscle adhesions, so it is often not corrected by plastic surgery.
If percutaneous balloon angioplasty cannot be performed or the treatment results are unsatisfactory, the mitral valve can be surgically repaired or replaced. Surgery for mitral stenosis consists of valvoplasty and valve replacement. In cases where the adhesion between the tendons and papillary muscles is relatively mild, mitral valve stenosis can be resolved through commissural incision and tendon excision in some cases. In most cases, the damage is so severe that mitral valve surgery is impossible, so valve replacement is performed. In consideration of the patient's age and life pattern, valve replacement is an operation that replaces a tissue valve that does not require anticoagulant medication (made from a pig or cow valve, pericardium, etc.) or a metal valve that requires lifelong anticoagulant medication after 6 months after surgery.
Prevent
Valve damage due to rheumatic fever, which was the main cause of mitral stenosis in the past, has been significantly reduced with the use of antibiotics, improved nutrition, and improved living standards such as housing facilities. The risk of endocarditis is very high in patients with valve disease or who have undergone valve replacement surgery, so prevention of infectious endocarditis is necessary. When receiving dental treatment or procedures for the urinary system, it is most important to tell the doctor about the condition of the valves and receive appropriate preventive antibiotic treatment before the procedure. However, conventional orthodontic treatment, caries treatment, and gastrointestinal endoscopy can be performed without additional preventive measures.
Diet/Life Guide
Regular exercise, such as walking, is recommended until severe heart failure develops. It is recommended to take treatment drugs regularly, to eat a low-sodium diet, to abstain from alcohol, and to quit smoking.